-
Need help?
+91 9311163794
-
Mail Us @
sales@subhotheaters.com
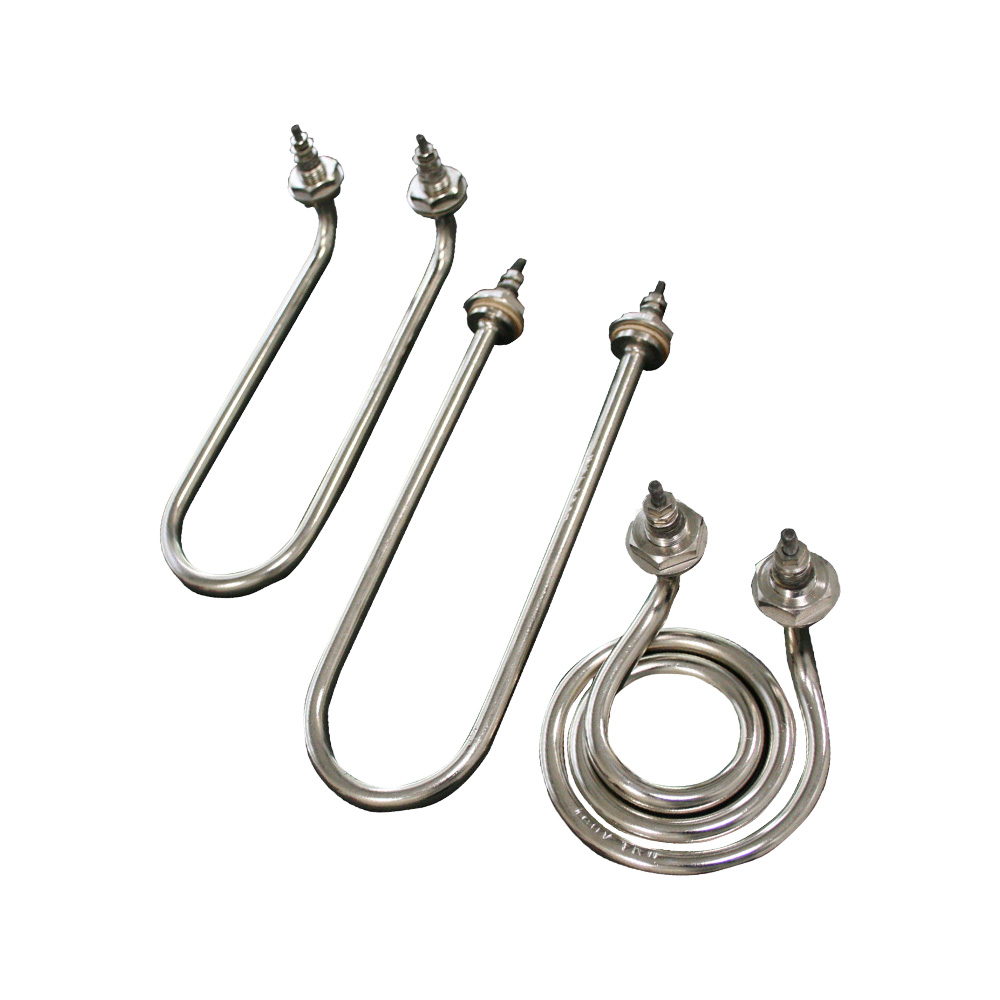
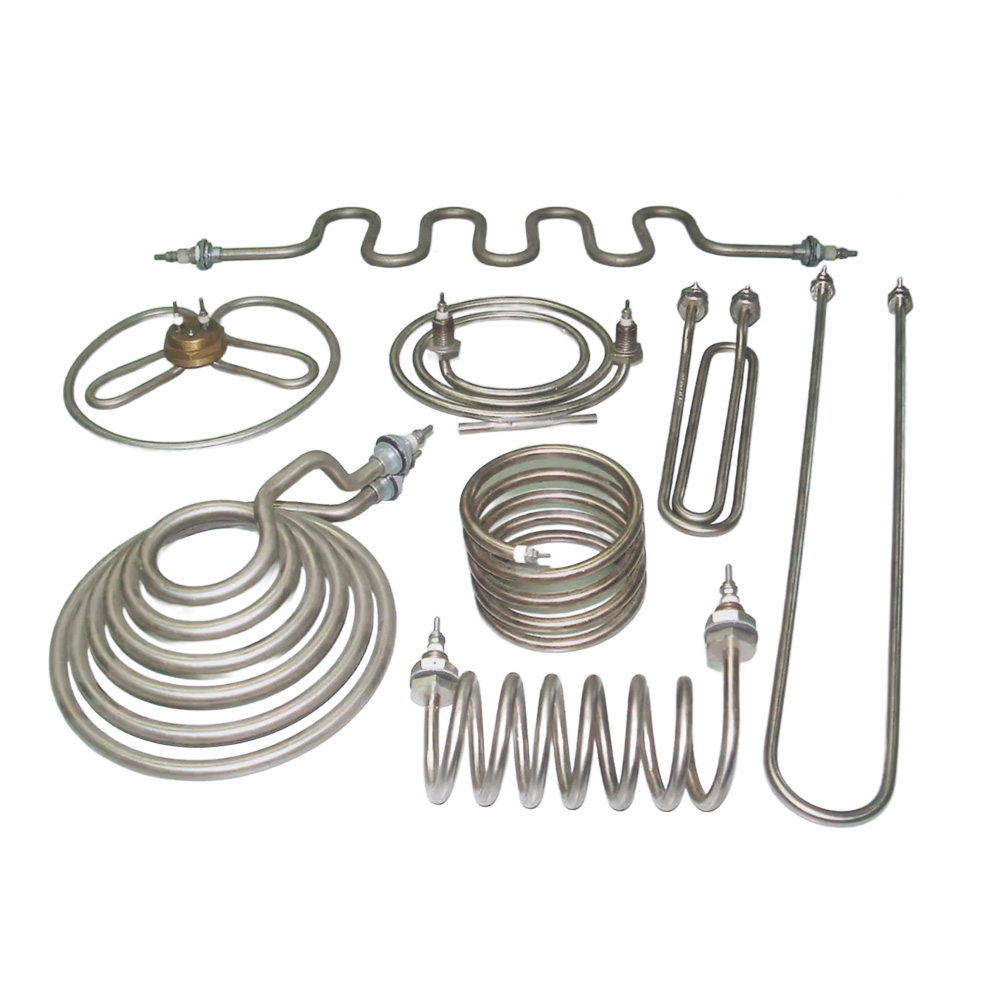
Tubular Heater


×
❮
![]()
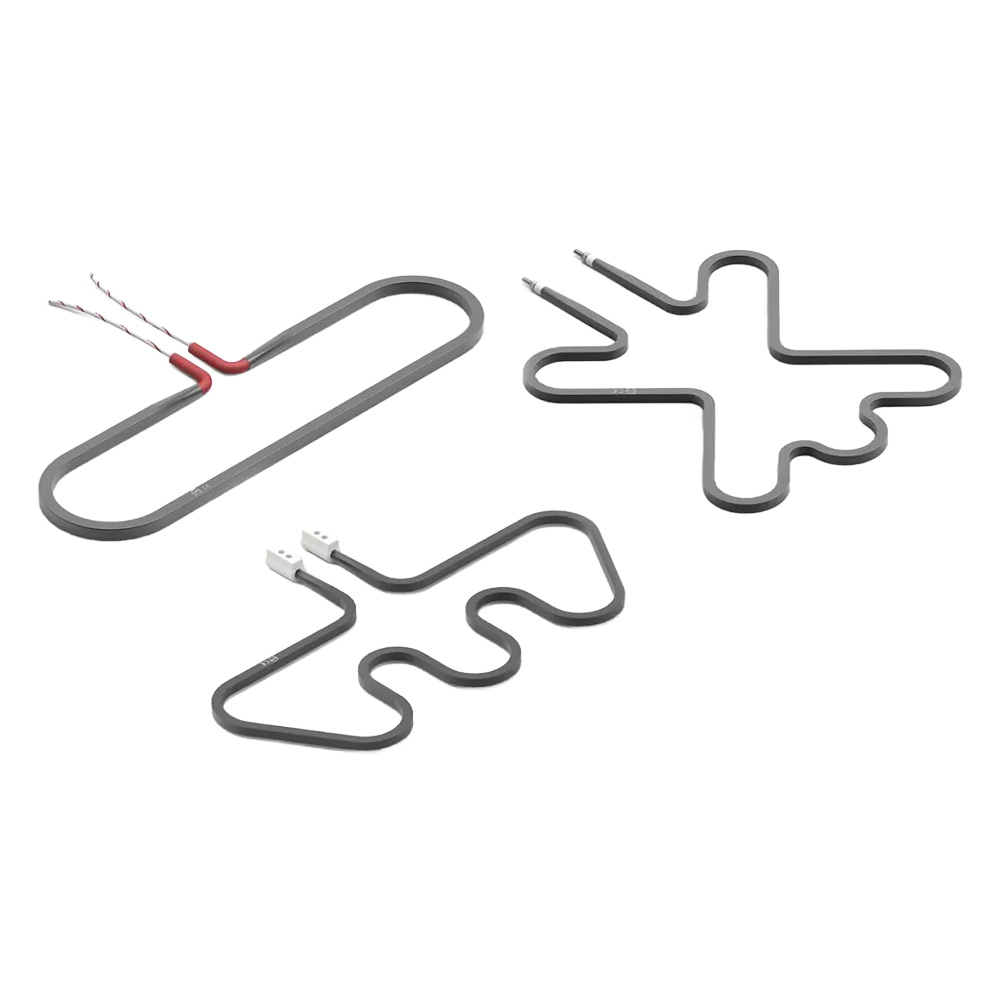
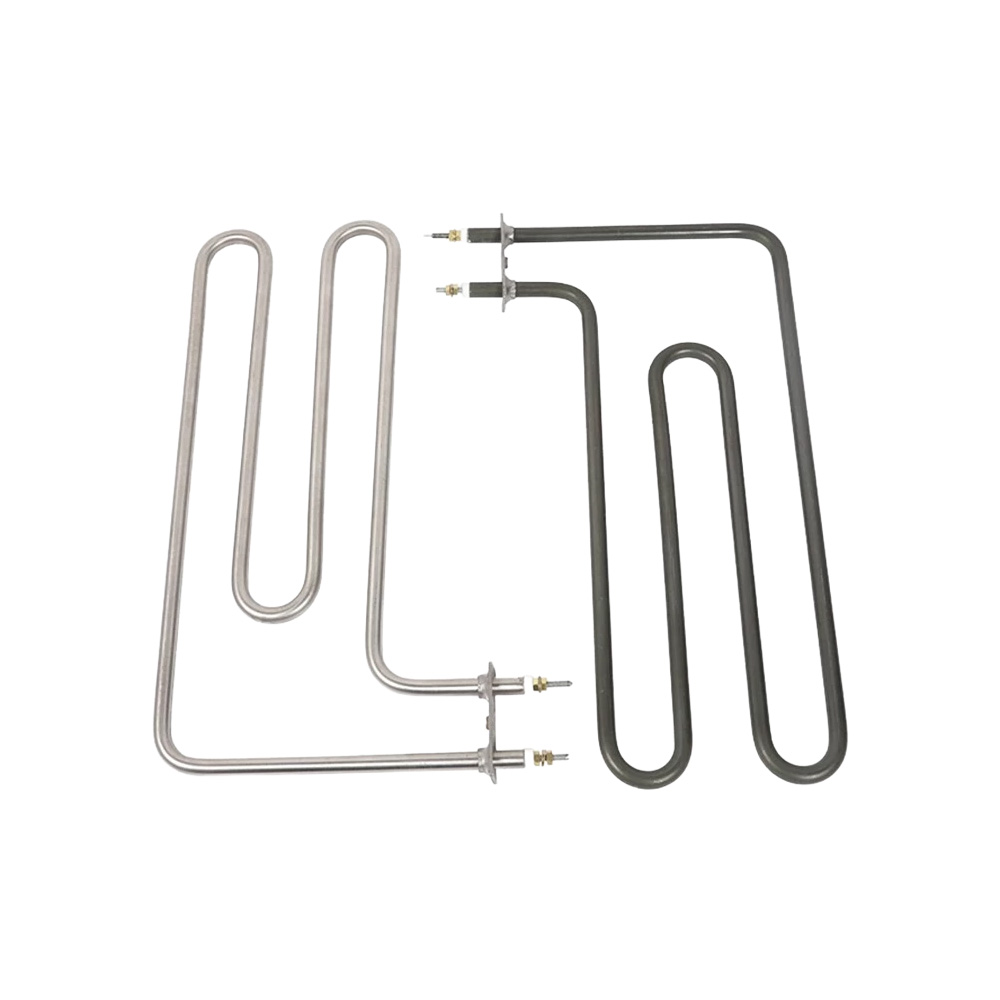
Tubular Heater
Tubular heaters are the most versatile and widely used industrial heating elements, designed for direct heating of air, liquids, solids, and surfaces. Built with a NiCr resistance wire insulated with high-purity magnesium oxide and encased in a metal sheath, they provide efficient heat transfer, durability, and uniform performance.
Available in straight, bent, or custom-formed shapes, tubular heaters are suitable for immersion, radiation, or conduction heating. Their adaptability, robust design, and long service life make them the standard choice for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
Advantages
- Highly Versatile – Suitable for air, liquid, and surface heating.
- Customizable Design – Available in straight, bent, or complex shapes.
- Efficient Heat Transfer – Conduction, convection, and radiation heating modes.
- Corrosion Resistance – Wide choice of sheath alloys for harsh environments.
- Rapid Heat-Up – Fast response with uniform heating.
- Durable Construction – Long service life with minimal maintenance.
Applications
- Air Heating – Ovens, dryers, and furnaces
- Liquid Heating – Immersion in tanks, baths, and process vessels.
- Plastics & Rubber – Mould heating and hot runner systems.
- Food Processing – Holding, cooking, and drying equipment.
- Packaging & Sealing – Heat-sealing and shrink systems.
- HVAC & Dehumidification – Heating coils and air conditioning systems.
- Medical – Sterilizers, autoclaves, and laboratory equipment.
Features
- Flexible Mounting – Can be designed in multiple orientations.
- Efficient Heat Transfer – Utilizes conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Uniform Heating – Ensures consistent temperature distribution.
- Corrosion & Oxidation Resistant – Built for industrial environments.
- Custom Sizes – Available up to 10 meters in length.
- Wide Power Range – Supports varied watt densities and voltages.







